Latest Sheet Music
Kenny Wheeler

Kenneth Vincent John Wheeler, OC (14 January 1930 – 18 September 2014) was a Canadian composer and trumpet and flugelhorn player, based in the U.K. from the 1950s onwards.
Most of his performances were rooted in jazz, but he was also active in free improvisation and occasionally contributed to rock music recordings. Wheeler wrote over one hundred compositions and was a skilled arranger for small groups and large ensembles.
Wheeler was the patron of the Royal Academy Junior Jazz course
Most of his performances were rooted in jazz, but he was also active in free improvisation and occasionally contributed to rock music recordings. Wheeler wrote over one hundred compositions and was a skilled arranger for small groups and large ensembles.
Wheeler was the patron of the Royal Academy Junior Jazz course
2PM

2PM is a South Korean boy band, originally a seven-member group, but currently consisting of six members due to sudden withdrawal of leader Jaebeom following an Internet controversy in September 2009. They are managed by JYP Entertainment. The current members are Junsu, Junho, Nichkhun, Taecyeon, Wooyoung and Chansung. 2PM is one of the two subgroups branched out from the eleven-member (before Jaebeom's departure) boy band One Day, the other being 2AM. They debuted with the song "10 Jeom Manjeome 10 Jeom" (10점 만점에 10점, lit. 10 Points Out of 10 Points), which showcased their acrobatic and b-boy dance styles. They achieved their first #1 song with "Again & Again".
Ludovico Einaudi

Ludovico Einaudi (born 23 November 1955) is an Italian contemporary classical music composer and pianist.
Although Einaudi would prefer not to be labeled as any particular type of genre, he is sometimes referred to as Minimalist. This is despite his music not sharing the key musical properties associated with minimalism. This may be due to his music possessing sparse orchestration and simplistic melodies that some may wish to refer to as 'minimalist' despite not belonging to the musical movement of Minimalism.
Einaudi's own words on the matter reflect this viewpoint, with Einaudi referring to Minimalism as "elegance and openness", despite its more formal definition as a musical movement to which he arguably does not belong.
Although Einaudi would prefer not to be labeled as any particular type of genre, he is sometimes referred to as Minimalist. This is despite his music not sharing the key musical properties associated with minimalism. This may be due to his music possessing sparse orchestration and simplistic melodies that some may wish to refer to as 'minimalist' despite not belonging to the musical movement of Minimalism.
Einaudi's own words on the matter reflect this viewpoint, with Einaudi referring to Minimalism as "elegance and openness", despite its more formal definition as a musical movement to which he arguably does not belong.
Apocalyptica

Apocalyptica is a Finnish cello metal band, composed of classically trained cellists and, since 2005, a drummer. Three of the cellists are graduates of the Sibelius Academy in Helsinki, Finland. Their music features elements from classical music, neo-classical metal, thrash metal, and symphonic metal.
Brahms

Johannes Brahms (May 7, 1833 â April 3, 1897) was a German composer of the Romantic period. He was born in Hamburg and in his later years he settled in Vienna, Austria.
Brahms maintained a Classical sense of form and order in his works â in contrast to the opulence of the music of many of his contemporaries. Thus many admirers (though not necessarily Brahms himself) saw him as the champion of traditional forms and "pure music," as opposed to the New German embrace of program music.
Brahms venerated Beethoven: in the composer's home, a marble bust of Beethoven looked down on the spot where he composed, and some passages in his works are reminiscent of Beethoven's style. The main theme of the finale of Brahms's First Symphony is reminiscent of the main theme of the finale of Beethoven's Ninth, and when this resemblance was pointed out to Brahms he replied that any ass â jeder Esel â could see that.
Ein deutsches Requiem was partially inspired by his mother's death in 1865, but also incorporates material from a Symphony he started in 1854, but abandoned following Schumann's suicide attempt. He once wrote that the Requiem "belonged to Schumann". The first movement of this abandoned Symphony was re-worked as the first movement of the First Piano Concerto.
Brahms also loved the Classical composers Mozart and Haydn. He collected first editions and autographs of their works, and edited performing editions. He also studied the music of pre-classical composers, including Giovanni Gabrieli, Johann Adolph Hasse, Heinrich Schütz and especially Johann Sebastian Bach. His friends included leading musicologists, and with Friedrich Chrysander he edited an edition of the works of François Couperin. He looked to older music for inspiration in the arts of strict counterpoint; the themes of some of his works are modelled on Baroque sources, such as Bach's The Art of Fugue in the fugal finale of Cello Sonata No. 1, or the same composer's Cantata No. 150 in the passacaglia theme of the Fourth Symphony's finale.
Brahms maintained a Classical sense of form and order in his works â in contrast to the opulence of the music of many of his contemporaries. Thus many admirers (though not necessarily Brahms himself) saw him as the champion of traditional forms and "pure music," as opposed to the New German embrace of program music.
Brahms venerated Beethoven: in the composer's home, a marble bust of Beethoven looked down on the spot where he composed, and some passages in his works are reminiscent of Beethoven's style. The main theme of the finale of Brahms's First Symphony is reminiscent of the main theme of the finale of Beethoven's Ninth, and when this resemblance was pointed out to Brahms he replied that any ass â jeder Esel â could see that.
Ein deutsches Requiem was partially inspired by his mother's death in 1865, but also incorporates material from a Symphony he started in 1854, but abandoned following Schumann's suicide attempt. He once wrote that the Requiem "belonged to Schumann". The first movement of this abandoned Symphony was re-worked as the first movement of the First Piano Concerto.
Brahms also loved the Classical composers Mozart and Haydn. He collected first editions and autographs of their works, and edited performing editions. He also studied the music of pre-classical composers, including Giovanni Gabrieli, Johann Adolph Hasse, Heinrich Schütz and especially Johann Sebastian Bach. His friends included leading musicologists, and with Friedrich Chrysander he edited an edition of the works of François Couperin. He looked to older music for inspiration in the arts of strict counterpoint; the themes of some of his works are modelled on Baroque sources, such as Bach's The Art of Fugue in the fugal finale of Cello Sonata No. 1, or the same composer's Cantata No. 150 in the passacaglia theme of the Fourth Symphony's finale.
The Crusaders

The Crusaders were an American jazz fusion group that was successful from the 1960s to the 1980s. The group was known as the Jazz Crusaders from its formation in 1960 until shortening its name in 1971.
Little Women

Little Women is a musical with a book by Allan Knee, lyrics by Mindi Dickstein, and music by Jason Howland.
Based on Louisa May Alcott's classic 1869 semi-autobiographical novel, it focuses on the four March sisters - feisty, tomboyish, aspiring author Jo, romantic Meg, pretentious Amy, and kind-hearted Beth - and their beloved Marmee, at home in Concord, Massachusetts while the family patriarch is away serving as a Union Army chaplain during the Civil War. Intercut with the vignettes in which their lives unfold are several recreations of the melodramatic short stories Jo writes in her attic studio.
After 55 previews, the Broadway production, directed by Susan H. Schulman, opened on January 23, 2005 at the Virginia Theatre where, hampered by reviews ranging from lukewarm to abrasive, it closed after 137 performances.
The cast included Sutton Foster, Maureen McGovern, Janet Carroll, Jenny Powers, Megan McGinnis, Amy McAlexander, Danny Gurwin, Autumn Hurlburt and John Hickok.
Based on Louisa May Alcott's classic 1869 semi-autobiographical novel, it focuses on the four March sisters - feisty, tomboyish, aspiring author Jo, romantic Meg, pretentious Amy, and kind-hearted Beth - and their beloved Marmee, at home in Concord, Massachusetts while the family patriarch is away serving as a Union Army chaplain during the Civil War. Intercut with the vignettes in which their lives unfold are several recreations of the melodramatic short stories Jo writes in her attic studio.
After 55 previews, the Broadway production, directed by Susan H. Schulman, opened on January 23, 2005 at the Virginia Theatre where, hampered by reviews ranging from lukewarm to abrasive, it closed after 137 performances.
The cast included Sutton Foster, Maureen McGovern, Janet Carroll, Jenny Powers, Megan McGinnis, Amy McAlexander, Danny Gurwin, Autumn Hurlburt and John Hickok.
Carter Burwell

Carter Burwell (born November 18, 1955) is an American composer of film scores.
Burwell was born in New York City. He graduated from King School in Stamford, Connecticut, and Harvard College.
As a film composer, Burwell has had a long working relationship with the Coen Brothers, providing music for every film they have made (except for O Brother, Where Art Thou?, where he simply provided additional music to a score primarily composed by T Bone Burnett). He enjoys working with left-field directors and has also scored Spike Jonze's films. Among his best known film scores are And the Band Played On (1993), Conspiracy Theory (1997), Hamlet (2000), The Spanish Prisoner (1997), Before the Devil Knows You're Dead (2007), In Bruges (2008) and Twilight (2008).
Burwell, like many composers, studied piano. Starting lessons when he was 7, he studied Mozart mostly, but eventually quit.
In April 2005, Burwell composed and conducted music, performed by The Parabola Ensemble, for the plays "Sawbones" written and directed by the Coen Brothers, "Hope Leaves the Theater" written and directed by Charlie Kaufman and "Anomalisa" written and directed by Francis Fregoli. This was a segment of the sound-only production Theater of the New Ear, which debuted at St. Ann's Warehouse in Brooklyn, NY with support from Sirius Satellite Radio, United Talent Agency and Sony Pictures.
Burwell married Christine Sciulli in 1999.
Burwell was born in New York City. He graduated from King School in Stamford, Connecticut, and Harvard College.
As a film composer, Burwell has had a long working relationship with the Coen Brothers, providing music for every film they have made (except for O Brother, Where Art Thou?, where he simply provided additional music to a score primarily composed by T Bone Burnett). He enjoys working with left-field directors and has also scored Spike Jonze's films. Among his best known film scores are And the Band Played On (1993), Conspiracy Theory (1997), Hamlet (2000), The Spanish Prisoner (1997), Before the Devil Knows You're Dead (2007), In Bruges (2008) and Twilight (2008).
Burwell, like many composers, studied piano. Starting lessons when he was 7, he studied Mozart mostly, but eventually quit.
In April 2005, Burwell composed and conducted music, performed by The Parabola Ensemble, for the plays "Sawbones" written and directed by the Coen Brothers, "Hope Leaves the Theater" written and directed by Charlie Kaufman and "Anomalisa" written and directed by Francis Fregoli. This was a segment of the sound-only production Theater of the New Ear, which debuted at St. Ann's Warehouse in Brooklyn, NY with support from Sirius Satellite Radio, United Talent Agency and Sony Pictures.
Burwell married Christine Sciulli in 1999.
Coldplay

Coldplay are a rock band formed in London, England in 1997. The group comprises vocalist/pianist/guitarist Chris Martin, lead guitarist Jonny Buckland, bassist Guy Berryman, and drummer/multi-instrumentalist Will Champion. Coldplay have sold 34.6 million albums, and are also known for their hit singles, such as "Yellow", "The Scientist", "Speed of Sound", "Fix You", "Viva la Vida" and the Grammy Award-winning "Clocks".
Coldplay achieved worldwide fame with the release of their single "Yellow", followed by their debut album, Parachutes (2000), which was nominated for the Mercury Prize. Its follow-up, A Rush of Blood to the Head (2002) won multiple awards such as NME's Album of the Year and was later included on Rolling Stone magazine's 500 Greatest Albums of All Time list, ranking at #473. Their next release, X&Y (2005), received a slightly less enthusiastic yet still generally positive reception. The band's fourth studio album, Viva la Vida or Death and All His Friends (2008), was produced by Brian Eno and released again to largely favourable reviews. All of Coldplay's albums have enjoyed great commercial success.
Coldplay's early material was compared to acts such as Jeff Buckley, U2, and Travis. Coldplay have been an active supporter of various social and political causes, such as Oxfam's Make Trade Fair campaign and Amnesty International. The group have also performed at various charity projects such as Band Aid 20, Live 8, and the Teenage Cancer Trust.
Coldplay achieved worldwide fame with the release of their single "Yellow", followed by their debut album, Parachutes (2000), which was nominated for the Mercury Prize. Its follow-up, A Rush of Blood to the Head (2002) won multiple awards such as NME's Album of the Year and was later included on Rolling Stone magazine's 500 Greatest Albums of All Time list, ranking at #473. Their next release, X&Y (2005), received a slightly less enthusiastic yet still generally positive reception. The band's fourth studio album, Viva la Vida or Death and All His Friends (2008), was produced by Brian Eno and released again to largely favourable reviews. All of Coldplay's albums have enjoyed great commercial success.
Coldplay's early material was compared to acts such as Jeff Buckley, U2, and Travis. Coldplay have been an active supporter of various social and political causes, such as Oxfam's Make Trade Fair campaign and Amnesty International. The group have also performed at various charity projects such as Band Aid 20, Live 8, and the Teenage Cancer Trust.
Igor Stravinsky

Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (17 June 1882 – 6 April 1971) was a Russian-born, naturalised French, later naturalised American composer, pianist, and conductor.
He is widely acknowledged as one of the most important and influential composers of 20th century music. He was a quintessentially cosmopolitan Russian who was named by Time magazine as one of the 100 most influential people of the century. He became a naturalised French citizen in 1934 and a naturalized US citizen in 1945. In addition to the recognition he received for his compositions, he also achieved fame as a pianist and a conductor, often at the premieres of his works.
Stravinsky's compositional career was notable for its stylistic diversity. He first achieved international fame with three ballets commissioned by the impresario Sergei Diaghilev and performed by Diaghilev's Ballets Russes (Russian Ballets): The Firebird (1910), Petrushka (1911/1947), and The Rite of Spring (1913). The Rite, whose premiere provoked a riot, transformed the way in which subsequent composers thought about rhythmic structure, and was largely responsible for Stravinsky's enduring reputation as a musical revolutionary, pushing the boundaries of musical design.
After this first Russian phase Stravinsky turned to neoclassicism in the 1920s. The works from this period tended to make use of traditional musical forms (concerto grosso, fugue, symphony), frequently concealed a vein of intense emotion beneath a surface appearance of detachment or austerity, and often paid tribute to the music of earlier masters, for example J.S. Bach and Tchaikovsky.
In the 1950s he adopted serial procedures, using the new techniques over his last twenty years. Stravinsky's compositions of this period share traits with examples of his earlier output: rhythmic energy, the construction of extended melodic ideas out of a few two- or three-note cells, and clarity of form, of instrumentation, and of utterance.
He also published a number of books throughout his career, almost always with the aid of a collaborator, sometimes uncredited. In his 1936 autobiography, Chronicles of My Life, written with the help of Walter Nouvel, Stravinsky included his well-known statement that "music is, by its very nature, essentially powerless to express anything at all." With Alexis Roland-Manuel and Pierre Souvtchinsky he wrote his 1939–40 Harvard University Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, which were delivered in French and later collected under the title Poétique musicale in 1942 (translated in 1947 as Poetics of Music). Several interviews in which the composer spoke to Robert Craft were published as Conversations with Igor Stravinsky. They collaborated on five further volumes over the following decade.
He is widely acknowledged as one of the most important and influential composers of 20th century music. He was a quintessentially cosmopolitan Russian who was named by Time magazine as one of the 100 most influential people of the century. He became a naturalised French citizen in 1934 and a naturalized US citizen in 1945. In addition to the recognition he received for his compositions, he also achieved fame as a pianist and a conductor, often at the premieres of his works.
Stravinsky's compositional career was notable for its stylistic diversity. He first achieved international fame with three ballets commissioned by the impresario Sergei Diaghilev and performed by Diaghilev's Ballets Russes (Russian Ballets): The Firebird (1910), Petrushka (1911/1947), and The Rite of Spring (1913). The Rite, whose premiere provoked a riot, transformed the way in which subsequent composers thought about rhythmic structure, and was largely responsible for Stravinsky's enduring reputation as a musical revolutionary, pushing the boundaries of musical design.
After this first Russian phase Stravinsky turned to neoclassicism in the 1920s. The works from this period tended to make use of traditional musical forms (concerto grosso, fugue, symphony), frequently concealed a vein of intense emotion beneath a surface appearance of detachment or austerity, and often paid tribute to the music of earlier masters, for example J.S. Bach and Tchaikovsky.
In the 1950s he adopted serial procedures, using the new techniques over his last twenty years. Stravinsky's compositions of this period share traits with examples of his earlier output: rhythmic energy, the construction of extended melodic ideas out of a few two- or three-note cells, and clarity of form, of instrumentation, and of utterance.
He also published a number of books throughout his career, almost always with the aid of a collaborator, sometimes uncredited. In his 1936 autobiography, Chronicles of My Life, written with the help of Walter Nouvel, Stravinsky included his well-known statement that "music is, by its very nature, essentially powerless to express anything at all." With Alexis Roland-Manuel and Pierre Souvtchinsky he wrote his 1939–40 Harvard University Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, which were delivered in French and later collected under the title Poétique musicale in 1942 (translated in 1947 as Poetics of Music). Several interviews in which the composer spoke to Robert Craft were published as Conversations with Igor Stravinsky. They collaborated on five further volumes over the following decade.
Count Basie

Count Basie Jazz pianist William "Count" Basie is an American jazz pianist, organist and jazz orchestra conductor.
Date of birth: August 21, 1904, Red Bank, New Jersey, USA Date and place of death: April 26, 1984, Hollywood, Florida, USA Instrument: Piano; Organ
Date of birth: August 21, 1904, Red Bank, New Jersey, USA Date and place of death: April 26, 1984, Hollywood, Florida, USA Instrument: Piano; Organ
Handel

George Frideric Handel (Friday, 23 February 1685 - Saturday, 14 April 1759) was a German-born Baroque composer who is famous for his operas, oratorios and concerti grossi. Born as Georg Friedrich Handel in Halle, he spent most of his adult life in England, becoming a subject of the British crown on 22 January 1727. His most famous works are Messiah, an oratorio set to texts from the King James Bible; Water Music; and Music for the Royal Fireworks. Strongly influenced by the techniques of the great composers of the Italian Baroque and the English composer Henry Purcell, his music was known to many significant composers who came after him, including Haydn, Mozart, and Beethoven.
Handel's compositions include 42 operas; 29 oratorios; more than 120 cantatas, trios and duets; numerous arias; chamber music; a large number of ecumenical pieces; odes and serenatas; and sixteen organ concerti. His most famous work, the Messiah oratorio with its "Hallelujah" chorus, is among the most popular works in choral music and has become a centerpiece of the Christmas season. Also popular are the Opus 3 and 6 Concerti Grossi, as well as "The Cuckoo and the Nightingale", in which birds are heard calling during passages played in different keys representing the vocal ranges of two birds. Also notable are his sixteen keyboard suites, especially The Harmonious Blacksmith.
Handel introduced various previously uncommon musical instruments in his works: the viola d'amore and violetta marina (Orlando), the lute (Ode for St. Cecilia's Day), three trombones (Saul), clarinets or small high cornets (Tamerlano), theorbo, French horn (Water Music), lyrichord, double bassoon, viola da gamba, bell chimes, positive organ, and harp (Giulio Cesare, Alexander's Feast).
Handel's compositions include 42 operas; 29 oratorios; more than 120 cantatas, trios and duets; numerous arias; chamber music; a large number of ecumenical pieces; odes and serenatas; and sixteen organ concerti. His most famous work, the Messiah oratorio with its "Hallelujah" chorus, is among the most popular works in choral music and has become a centerpiece of the Christmas season. Also popular are the Opus 3 and 6 Concerti Grossi, as well as "The Cuckoo and the Nightingale", in which birds are heard calling during passages played in different keys representing the vocal ranges of two birds. Also notable are his sixteen keyboard suites, especially The Harmonious Blacksmith.
Handel introduced various previously uncommon musical instruments in his works: the viola d'amore and violetta marina (Orlando), the lute (Ode for St. Cecilia's Day), three trombones (Saul), clarinets or small high cornets (Tamerlano), theorbo, French horn (Water Music), lyrichord, double bassoon, viola da gamba, bell chimes, positive organ, and harp (Giulio Cesare, Alexander's Feast).
Tchaikovsky

Pyotr Il'yich Tchaikovsky (May 7 1840 â November 6 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic era. While not part of the nationalistic music group known as "The Five", Tchaikovsky wrote music which, in the opinion of Harold Schonberg, was distinctly Russian: plangent, introspective, with modally-inflected melody and harmony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Aesthetically, Tchaikovsky remained open to all aspects of Saint Petersburg musical life. He was impressed by Serov and Balakirev as well as the classical values upheld by the conservatory. Both the progressive and conservative camps in Russian music at the time attempted to win him over. Tchaikovsky charted his compositional course between these two factions, retaining his individuality as a composer as well as his Russian identity. In this he was influenced by the ideals of his teacher Nikolai Rubinstein and Nikolai's brother Anton.
Tchaikovsky's musical cosmopolitanism led him to be favored by many Russian music-lovers over the "Russian" harmonies and styles of Mussorgsky, Borodin and Rimsky-Korsakov.
Nonetheless he frequently adapted Russian traditional melodies and dance forms in his music, which enhanced his success in his home country. The success in St. Petersburg at the premiere of his Third Orchestral Suite may have been due in large part to his concluding the work with a polonaise. He also used a polonaise for the final movement of his Third Symphony.
Masato Nakamura

Masato Nakamura is a Japanese musician, bass player and record producer. Founded in 1988, J-pop is a member of Dreams Come True, which continues to sell more than 50 million CDs. Sonic the Hedgehog and Sonic the Hedgehog 2 are known outside of Japan for composing video game soundtracks.
Rachmaninoff

Sergei Vasilievich Rachmaninoff (1 April 1873 - 28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor. He was one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, the last great representative of Russian late Romanticism in classical music. Early influences of Tchaikovsky, Rimsky-Korsakov and other Russian composers gave way to a thoroughly personal idiom which included a pronounced lyricism, expressive breadth, structural ingenuity and a tonal palette of rich, distinctive orchestral colors.
Understandably, the piano figures prominently in Rachmaninoff's compositional output, either as a solo instrument or as part of an ensemble. He made it a point, however, to use his own skills as a performer to explore fully the expressive possibilities of the instrument. Even in his earliest works, he revealed a sure grasp of idiomatic piano writing and a striking gift for melody. In some of his early orchestral pieces he showed the first signs of a talent for tone painting, which he would perfect in The Isle of the Dead, and he began to show a similar penchant for vocal writing in two early sets of songs, Opp. 4 and 8. Rachmaninoff's masterpiece, however, is his choral symphony The Bells, in which all of his talents are fused and unified.
Rachmaninoff sometimes felt threatened by the success of modernists such as Scriabin and Prokofiev and wondered whether to cease composing even before he left Russia. His musical philosophy was rooted in the Russian spiritual tradition, where the role of the artist was to create beauty and to speak the truth from the depths of his heart. In his last major interview, in 1941, he admitted his music, like Russian music, was a product of his temperament. He said, on another occasion, "The new kind of music seems to create not from the heart but from the head. Its composers think rather than feel. They have not the capacity to make their works exalt—they meditate, protest, analyze, reason, calculate and brood, but they do not exalt."
Understandably, the piano figures prominently in Rachmaninoff's compositional output, either as a solo instrument or as part of an ensemble. He made it a point, however, to use his own skills as a performer to explore fully the expressive possibilities of the instrument. Even in his earliest works, he revealed a sure grasp of idiomatic piano writing and a striking gift for melody. In some of his early orchestral pieces he showed the first signs of a talent for tone painting, which he would perfect in The Isle of the Dead, and he began to show a similar penchant for vocal writing in two early sets of songs, Opp. 4 and 8. Rachmaninoff's masterpiece, however, is his choral symphony The Bells, in which all of his talents are fused and unified.
Rachmaninoff sometimes felt threatened by the success of modernists such as Scriabin and Prokofiev and wondered whether to cease composing even before he left Russia. His musical philosophy was rooted in the Russian spiritual tradition, where the role of the artist was to create beauty and to speak the truth from the depths of his heart. In his last major interview, in 1941, he admitted his music, like Russian music, was a product of his temperament. He said, on another occasion, "The new kind of music seems to create not from the heart but from the head. Its composers think rather than feel. They have not the capacity to make their works exalt—they meditate, protest, analyze, reason, calculate and brood, but they do not exalt."
Muse

Muse are a British rock band formed in Teignmouth, Devon, United Kingdom in 1994 under the alias of Rocket Baby Dolls. The band comprises Matthew Bellamy (vocals, guitar and piano), Christopher Wolstenholme (bass guitar and backing vocals) and Dominic Howard (drums and percussion). Muse's style can be considered as a mixture of many musical genres, most notably alternative rock, classical music and electronica. Muse are known best for their energetic and visually dazzling live performances and on June 16th & 17th, 2007 became the first band to sell out the newly built Wembley Stadium in London. Muse have released four studio albums with their first, Showbiz, released in 1999, followed by Origin of Symmetry in 2001 and Absolution in 2003. The most recent, Black Holes & Revelations (2006), was also the most critically acclaimed, garnering the band a Mercury Prize nomination and a third place finish in the NME Albums of the Year list for 2006. Muse have won various awards throughout their career including 5 MTV Europe Music Awards, 5 Q Awards, 4 NME Awards and 2 Brit awards.
Lee Morgan

Lee Morgan (July 10, 1938 – February 19, 1972) was an American jazz trumpeter and composer.
One of the key hard bop musicians of the 1960s, Morgan came to prominence in his late teens, recording on John Coltrane's Blue Train (1957) and with the band of drummer Art Blakey before launching a solo career. Morgan stayed with Blakey until 1961 and started to record as leader soon after. His song "The Sidewinder", on the album of the same name, became a surprise crossover hit on the pop and R&B charts in 1964, while Morgan's recordings found him touching on other styles of music as his artistry matured. Soon after The Sidewinder was released, Morgan rejoined Blakey for a short period. After leaving Blakey for the final time, Morgan continued to work prolifically as both a leader and a sideman with the likes of Hank Mobley and Wayne Shorter, becoming a cornerstone of the Blue Note label.
One of the key hard bop musicians of the 1960s, Morgan came to prominence in his late teens, recording on John Coltrane's Blue Train (1957) and with the band of drummer Art Blakey before launching a solo career. Morgan stayed with Blakey until 1961 and started to record as leader soon after. His song "The Sidewinder", on the album of the same name, became a surprise crossover hit on the pop and R&B charts in 1964, while Morgan's recordings found him touching on other styles of music as his artistry matured. Soon after The Sidewinder was released, Morgan rejoined Blakey for a short period. After leaving Blakey for the final time, Morgan continued to work prolifically as both a leader and a sideman with the likes of Hank Mobley and Wayne Shorter, becoming a cornerstone of the Blue Note label.
Counting Crows

Counting Crows is a rock band originating from Berkeley, California. The group gained popularity in 1994 following the release of its debut album August and Everything After, which featured the hit single "Mr. Jones". The band's influences include Van Morrison, R.E.M., Nirvana, Bob Dylan, and The Band. They received a 2004 Academy Award nomination for the song "Accidentally in Love".
T-Pain

Faheem Rasheed Najm, (born September 30, 1985 in Tallahassee, Florida) better known by his stage name T-Pain, is an American hip hop and R&B singer-songwriter and producer. He has been noted for using autotune.
He was born in to entrepreneur Christian parents, Najib Shasheem and Aliyah Najm, and was brought up Muslim. At the age of ten, Faheem reworked his bedroom into a small studio with a keyboard, beat machine and four-track recorder, and began composing music. Faheem later graduated from James S. Rickards High School in Tallahassee, Florida Prior to becoming a solo singer, Faheem was part of the Tallahassee rap group Nappy Headz (OD, Notty Black, Nook DogG, Doeboy), allowing T-Pain to start his career as a rapper. T-Pain has said in an interview to MSNBC that Akon "called me right when I went to get my application from McDonald’s". After the phone call history was made. In 2002, he founded his own style of musicl, Hard & B, and soon caught the spotlight as a solo artist when his song "I'm Fucked Up", a reworked version of Akon's "Locked Up", gained popularity in the region. Akon noticed the song and signed T-Pain to his newly formed Konvict Music record label.
He was born in to entrepreneur Christian parents, Najib Shasheem and Aliyah Najm, and was brought up Muslim. At the age of ten, Faheem reworked his bedroom into a small studio with a keyboard, beat machine and four-track recorder, and began composing music. Faheem later graduated from James S. Rickards High School in Tallahassee, Florida Prior to becoming a solo singer, Faheem was part of the Tallahassee rap group Nappy Headz (OD, Notty Black, Nook DogG, Doeboy), allowing T-Pain to start his career as a rapper. T-Pain has said in an interview to MSNBC that Akon "called me right when I went to get my application from McDonald’s". After the phone call history was made. In 2002, he founded his own style of musicl, Hard & B, and soon caught the spotlight as a solo artist when his song "I'm Fucked Up", a reworked version of Akon's "Locked Up", gained popularity in the region. Akon noticed the song and signed T-Pain to his newly formed Konvict Music record label.
Vivaldi

Antonio Lucio Vivaldi (March 4, 1678 â July 28, 1741), nicknamed il Prete Rosso ("The Red Priest"), was a Venetian priest and Baroque music composer, as well as a famous virtuoso violinist; he was born and raised in the Republic of Venice. The Four Seasons, a series of four violin concerti, is his best-known work and a highly popular Baroque piece.
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Many of Vivaldi's compositions reflect a flamboyant, almost playful, exuberance. Most of Vivaldi's repertoire was rediscovered only in the first half of the 20th century in Turin and Genoa and was published in the second half. Vivaldi's music is innovative, breaking a consolidated tradition in schemes; he gave brightness to the formal and the rhythmic structure of the concerto, repeatedly looking for harmonic contrasts and innovative melodies and themes. Moreover, Vivaldi was able to compose nonacademic music, particularly meant to be appreciated by the wide public and not only by an intellectual minority. The joyful appearance of his music reveals in this regard a transmissible joy of composing; these are among the causes of the vast popularity of his music. This popularity soon made him famous in other countries such as France which was, at the time, very independent concerning its musical taste.
Vivaldi is considered one of the composers who brought Baroque music (with its typical contrast among heavy sonorities) to evolve into a classical style. Johann Sebastian Bach was deeply influenced by Vivaldi's concertos and arias (recalled in his Johannes Passion, Matthäuspassion, and cantatas). Bach transcribed a number of Vivaldi's concerti for solo keyboard, along with a number for orchestra, including the famous Concerto for Four Violins and Violoncello, Strings and Continuo (RV 580).
Georges Bizet

Georges Bizet (25 October 1838 – 3 June 1875) was a French composer and pianist of the Romantic era. He is best known for the opera Carmen.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Bizet was born at 26 rue de la Tour d'Auvergne in the 9th arrondissement of Paris in 1838. He was registered with the legal name Alexandre César Léopold Bizet, but he was baptised on 16 March 1840 with the first name Georges, and he was always known thereafter as Georges Bizet. His father Adolphe Armand Bizet (1810-86) was an amateur singer and composer, and his mother, Aimée Léopoldine Joséphine née Delsarte (1814-61), was the sister of the famous singing teacher François Delsarte.
He entered the Paris Conservatory of Music on 9 October 1848, a fortnight before his tenth birthday. His teachers there were Pierre Zimmermann (fugue and counterpoint; often assisted by his son-in-law Charles Gounod), Antoine François Marmontel (piano), François Benoist (organ) and, on Zimmermann's death, Fromental Halévy, whose daughter he himself later married. He won first prizes for organ and fugue in 1855 and completed his earliest compositions.
His first symphony, the Symphony in C, was written in November 1855, when he was seventeen, evidently as a student assignment. It was unknown to the world until 1933, when it was discovered in the archives of the Paris Conservatory library. Upon its first performance in 1935, it was immediately hailed as a junior masterwork and a welcome addition to the early Romantic period repertoire. The symphony bears a stylistic resemblance to the first symphony of Gounod, first played earlier in the same year, and which Bizet had arranged for two pianos although present-day listeners may discern a similarity to music of Franz Schubert, whose work was little known in France at the time the symphony was written.
In 1857, a setting of the one-act operetta Le docteur Miracle won him a share in a prize offered by Jacques Offenbach. He also won the music composition scholarship of the Prix de Rome, the conditions of which required him to study in Rome for three years. There, his talent developed as he wrote such works as the opera buffa Don Procopio (1858-59). There he also composed his only major sacred work, Te Deum (1858), which he submitted to the Prix Rodrigues competition, a contest for Prix de Rome winners only. Bizet failed to win the Prix Rodrigues, and the Te Deum score remained unpublished until 1971. He made two attempts to write another symphony in 1859, but destroyed the manuscripts in December of that year. Apart from this period in Rome, Bizet lived in the Paris area all his life.
Shortly after leaving Rome in July 1860, but while still touring in Italy, he had the idea of writing a symphony in which each of the four movements would be a musical evocation of a different Italian city – Rome, Venice, Florence and Naples. On hearing of his mother's serious illness he cut short his Italian travels and returned to Paris in September 1860; she died a year later. The Scherzo of the symphony was completed by November 1861, but it was not until 1866 that the first version of the whole symphony was written. He subjected it to a number of revisions through to 1871, but died before ever producing what he considered the definitive version. For this reason, the work is sometimes described as "unfinished", but this is an inaccurate description as it was fully scored. It was published in 1880 as the Roma Symphony.
Wagner Ortiz

Wagner Ortiz, flutist, composer, teacher and poet began his studies with maestro Valdir Peruzetto and Gilberto dos Santos, then studied flute at the Universidade Livre de Música - Tom Jobim under the guidance of master Marcos Kiehl. He started his studies in composition as a self-taught, later he was guided by the German conductor H.J. Koellreutter and prof. Sérgio Villafranca. With maestro Marcos Murilo de Almeida Passos, he taught MPB functional and aesthetic harmony lessons. He also conducted studies on Brazilian folk music with maestro Ubiratan Sousa and Lyrical singing with Solange Gonçalves.
Frank Sinatra

Francis Albert "Frank" Sinatra (December 12, 1915 â May 14, 1998) was an American singer and actor.
Beginning his musical career in the swing era with Harry James and Tommy Dorsey, Sinatra became a solo artist with great success in the early to mid-1940s, being the idol of the "bobby soxers". His professional career had stalled by the 1950s, but it was reborn in 1954 after he won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor.
He signed with Capitol Records and released several critically lauded albums (such as In the Wee Small Hours, Songs for Swingin' Lovers, Come Fly with Me, Only the Lonely and Nice 'n' Easy). Sinatra left Capitol to found his own record label, Reprise Records (finding success with albums such as Ring-A-Ding-Ding, Sinatra at the Sands and Francis Albert Sinatra & Antonio Carlos Jobim), toured internationally, and fraternized with the Rat Pack and President John F. Kennedy in the early 1960s. Sinatra turned 50 in 1965, recorded the retrospective September of My Years, starred in the Emmy-winning television special Frank Sinatra: A Man and His Music, and scored hits with "Strangers in the Night" and "My Way".
Sinatra attempted to weather the changing tastes in popular music, but with dwindling album sales and after appearing in several poorly received films, he retired in 1971. Coming out of retirement in 1973, he recorded several albums, scoring a hit with "(Theme From) New York, New York" in 1980, and toured both within the United States and internationally until a few years before his death in 1998.
Sinatra also forged a career as a dramatic actor, winning the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performance in From Here to Eternity, and he was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor for The Man with the Golden Arm. His also starred in such musicals as High Society, Pal Joey, Guys and Dolls and On the Town. Sinatra was honored with the Kennedy Center Honors in 1983 and awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Ronald Reagan in 1985 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 1997. Sinatra was also the recipient of eleven Grammy Awards, including the Grammy Trustees Award, Grammy Legend Award and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Beginning his musical career in the swing era with Harry James and Tommy Dorsey, Sinatra became a solo artist with great success in the early to mid-1940s, being the idol of the "bobby soxers". His professional career had stalled by the 1950s, but it was reborn in 1954 after he won the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor.
He signed with Capitol Records and released several critically lauded albums (such as In the Wee Small Hours, Songs for Swingin' Lovers, Come Fly with Me, Only the Lonely and Nice 'n' Easy). Sinatra left Capitol to found his own record label, Reprise Records (finding success with albums such as Ring-A-Ding-Ding, Sinatra at the Sands and Francis Albert Sinatra & Antonio Carlos Jobim), toured internationally, and fraternized with the Rat Pack and President John F. Kennedy in the early 1960s. Sinatra turned 50 in 1965, recorded the retrospective September of My Years, starred in the Emmy-winning television special Frank Sinatra: A Man and His Music, and scored hits with "Strangers in the Night" and "My Way".
Sinatra attempted to weather the changing tastes in popular music, but with dwindling album sales and after appearing in several poorly received films, he retired in 1971. Coming out of retirement in 1973, he recorded several albums, scoring a hit with "(Theme From) New York, New York" in 1980, and toured both within the United States and internationally until a few years before his death in 1998.
Sinatra also forged a career as a dramatic actor, winning the Academy Award for Best Supporting Actor for his performance in From Here to Eternity, and he was nominated for the Academy Award for Best Actor for The Man with the Golden Arm. His also starred in such musicals as High Society, Pal Joey, Guys and Dolls and On the Town. Sinatra was honored with the Kennedy Center Honors in 1983 and awarded the Presidential Medal of Freedom by Ronald Reagan in 1985 and the Congressional Gold Medal in 1997. Sinatra was also the recipient of eleven Grammy Awards, including the Grammy Trustees Award, Grammy Legend Award and the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award.
Falú, Eduardo

Eduardo Falú Argentine musical composer DescriptionEduardo Falú was a well-known Argentine folk music guitarist and composer. Born: July 7, 1923, El Galpón, Salta, Argentina died: August 9, 2013, Córdoba, Argentina Instrument: Guitar
Albums: Romance De La Muerte De Juan Lavalle, MORE Movies: Bajo el signo de la patria, Cerro Guanaco, MORE
Albums: Romance De La Muerte De Juan Lavalle, MORE Movies: Bajo el signo de la patria, Cerro Guanaco, MORE
Michael Giacchino

Michael Giacchino (Italian pronunciation: ; born October 10, 1967) is an American composer who has composed scores for movies, television series and video games. Some of his most notable works include the scores to television series such as Lost, Alias and Fringe, games such as the Medal of Honor and Call of Duty series, and films such as Mission: Impossible III, The Incredibles, Star Trek, Star Trek Into Darkness, Cloverfield, Ratatouille, Up, Super 8, Cars 2, 50/50, and John Carter. Giacchino has received numerous awards for his work, including an Emmy, multiple Grammys, a Golden Globe Award, and an Academy Award.
Mauro Giuliani

Mauro Giuseppe Sergio Pantaleo Giuliani (July 27, 1781 – May 8, 1829) was an Italian guitarist and composer, and is considered by many to be one of the leading guitar virtuosi of the early 19th century.
J. S. Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (21 March 1685, O.S.31 March 1685, N.S. – 28 July 1750, N.S.) was a German composer, organist, harpsichordist, violist, and violinist whose sacred and secular works for choir, orchestra, and solo instruments drew together the strands of the Baroque period and brought it to its ultimate maturity. Although he did not introduce new forms, he enriched the prevailing German style with a robust contrapuntal technique, an unrivalled control of harmonic and motivic organisation, and the adaptation of rhythms, forms and textures from abroad, particularly from Italy and France.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Revered for their intellectual depth, technical command and artistic beauty, Bach's works include the Brandenburg Concertos, the Goldberg Variations, the Partitas, The Well-Tempered Clavier, the Mass in B minor, the St Matthew Passion, the St John Passion, the Magnificat, A Musical Offering, The Art of Fugue, the English and French Suites, the Sonatas and Partitas for solo violin, the Cello Suites, more than 200 surviving cantatas, and a similar number of organ works, including the famous Toccata and Fugue in D minor and Passacaglia and Fugue in C minor, as well as the Great Eighteen Chorale Preludes and Organ Mass.
Bach's abilities as an organist were highly respected throughout Europe during his lifetime, although he was not widely recognised as a great composer until a revival of interest and performances of his music in the first half of the 19th century. He is now generally regarded as one of the main composers of the Baroque style, and as one of the greatest composers of all time.
Pink Floyd

Pink Floyd are an English rock band from Cambridge. The band initially earned recognition for their psychedelic and space rock music, and, as they evolved, for their progressive rock music. Pink Floyd are known for philosophical lyrics, sonic experimentation, innovative album cover art, and elaborate live shows. One of rock music's most successful acts, the group have sold over 200 million albums worldwide including 74.5 million albums in the United States alone. Pink Floyd have influenced progressive rock artists of the 1970s such as Genesis and Yes; and contemporary artists such as Nine Inch Nails and Dream Theater.
Pink Floyd had moderate mainstream success and were one of the most popular bands in the London underground music scene in the late 1960s as a psychedelic band led by Syd Barrett. However, Barrett's erratic behaviour eventually forced his colleagues to replace him with guitarist and singer David Gilmour. After Barrett's departure, singer and bass player Roger Waters gradually became the dominant and driving force in the group by the late-1970s, until his eventual departure from the group in 1985. The band recorded several albums, achieving worldwide success with The Dark Side of the Moon (1973), Wish You Were Here (1975), Animals (1977), and The Wall (1979).
In 1985, Waters declared Pink Floyd "a spent force", but the remaining members, led by Gilmour, continued recording and touring under the name Pink Floyd. Waters sued them for the name and eventually they reached a settlement out of court, under which Gilmour, Mason and Wright would continue as Pink Floyd. They again enjoyed worldwide success with A Momentary Lapse of Reason (1987) and The Division Bell (1994). Waters performed with the band for the first time in 24 years on 2 July 2005 at the London Live 8 concert.
Pink Floyd had moderate mainstream success and were one of the most popular bands in the London underground music scene in the late 1960s as a psychedelic band led by Syd Barrett. However, Barrett's erratic behaviour eventually forced his colleagues to replace him with guitarist and singer David Gilmour. After Barrett's departure, singer and bass player Roger Waters gradually became the dominant and driving force in the group by the late-1970s, until his eventual departure from the group in 1985. The band recorded several albums, achieving worldwide success with The Dark Side of the Moon (1973), Wish You Were Here (1975), Animals (1977), and The Wall (1979).
In 1985, Waters declared Pink Floyd "a spent force", but the remaining members, led by Gilmour, continued recording and touring under the name Pink Floyd. Waters sued them for the name and eventually they reached a settlement out of court, under which Gilmour, Mason and Wright would continue as Pink Floyd. They again enjoyed worldwide success with A Momentary Lapse of Reason (1987) and The Division Bell (1994). Waters performed with the band for the first time in 24 years on 2 July 2005 at the London Live 8 concert.
Green Day

Green Day is an American rock trio formed in 1987. The band has consisted of Billie Joe Armstrong (vocals, guitar), Mike Dirnt (bass guitar, vocals), and Tré Cool (drums, percussion) for the majority of its existence.
Green Day was originally part of the punk rock scene at 924 Gilman Street in Berkeley, California. Its early releases for independent record label Lookout! Records earned them a grassroots fanbase, some of whom felt alienated when the band signed to a major label.
The band has sold over 65 million records worldwide, They also have three Grammy Awards, Best Alternative Album for Dookie, Best Rock Album for American Idiot, and Record of the Year for "Boulevard of Broken Dreams".
Green Day was originally part of the punk rock scene at 924 Gilman Street in Berkeley, California. Its early releases for independent record label Lookout! Records earned them a grassroots fanbase, some of whom felt alienated when the band signed to a major label.
The band has sold over 65 million records worldwide, They also have three Grammy Awards, Best Alternative Album for Dookie, Best Rock Album for American Idiot, and Record of the Year for "Boulevard of Broken Dreams".
Justin Bieber

Justin Bieber (pronounced /ˈbiːbər/, BEE-bər; born March 1, 1994) is a Canadian pop/R&B singer. His performances on YouTube were seen by Scooter Braun, who later became his manager. Braun arranged for him to meet with Usher in Atlanta, Georgia, and Bieber was soon signed to Raymond Braun Media Group (RBMG), a joint venture between Braun and Usher, and then to a recording contract with Island Records offered by L.A. Reid.
His debut single, "One Time", was released worldwide during 2009, and charted within the top thirty in over ten countries. It was followed by his debut release, My World on November 17, 2009, which was certified platinum in the United States, which at the time gave Bieber the highest debut by a new artist in the year, and made Bieber the first artist to have seven songs from a debut album chart on Billboard's Hot 100 chart. His first full studio release, My World 2.0 was released on March 23, 2010, debuting at number one and within the top ten of several countries. It was preceded by the international hit song, "Baby".
His debut single, "One Time", was released worldwide during 2009, and charted within the top thirty in over ten countries. It was followed by his debut release, My World on November 17, 2009, which was certified platinum in the United States, which at the time gave Bieber the highest debut by a new artist in the year, and made Bieber the first artist to have seven songs from a debut album chart on Billboard's Hot 100 chart. His first full studio release, My World 2.0 was released on March 23, 2010, debuting at number one and within the top ten of several countries. It was preceded by the international hit song, "Baby".
Bart Howard

Bart Howard (born Howard Joseph Gustafson; June 1, 1915 — February 21, 2004) was the composer and writer of the famous jazz standard "Fly Me To The Moon", which has been performed by singers (among others) Frank Sinatra, Ella Fitzgerald, Nancy Wilson, Della Reese, Diana Krall, June Christy and Astrud Gilberto. It is also played frequently by jazz and popular musicians around the world.
Howard was born in Burlington, Iowa. He began his career as an accompanist at the age of 16 and played for Mabel Mercer, Johnny Mathis and Eartha Kitt, among others.
"Fly Me To the Moon" was first sung in 1954 by Felicia Sanders at the "Blue Angel" club in Manhattan where the composer became M.C. and accompanist in 1951. The song received wide exposure when Peggy Lee sang it on The Ed Sullivan Show several years later. Bart Howard "lived off" this song for the rest of his life, although he had 49 other songs to his credit.
He died, aged 88, in Carmel, New York. He was survived by a sister Dorothy Lind of Burlington, Iowa and by his companion of 58 years, Thomas Fowler.
Howard was born in Burlington, Iowa. He began his career as an accompanist at the age of 16 and played for Mabel Mercer, Johnny Mathis and Eartha Kitt, among others.
"Fly Me To the Moon" was first sung in 1954 by Felicia Sanders at the "Blue Angel" club in Manhattan where the composer became M.C. and accompanist in 1951. The song received wide exposure when Peggy Lee sang it on The Ed Sullivan Show several years later. Bart Howard "lived off" this song for the rest of his life, although he had 49 other songs to his credit.
He died, aged 88, in Carmel, New York. He was survived by a sister Dorothy Lind of Burlington, Iowa and by his companion of 58 years, Thomas Fowler.
Jimmy Smith

James Oscar Smith (December 8, 1925 or 1928 – February 8, 2005) was an American jazz musician whose albums often charted on Billboard magazine. He helped popularize the Hammond B-3 organ, creating a link between jazz and 1960s soul music.
In 2005, Smith was awarded the NEA Jazz Masters Award from the National Endowment for the Arts, the highest honor that America bestows upon jazz musicians.
In 2005, Smith was awarded the NEA Jazz Masters Award from the National Endowment for the Arts, the highest honor that America bestows upon jazz musicians.
Guiseppe Verdi

Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi (Italian pronunciation: ; 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian Romantic composer, mainly of opera. He was one of the most influential composers of the 19th century. His works are frequently performed in opera houses throughout the world and, transcending the boundaries of the genre, some of his themes have long since taken root in popular culture - such as "La donna è mobile" from Rigoletto, "Va, pensiero" (The Chorus of the Hebrew Slaves) from Nabucco, "Libiamo ne' lieti calici" (The Drinking Song) from La traviata and the "Grand March" from Aida. Although his work was sometimes criticized for using a generally diatonic rather than a chromatic musical idiom and having a tendency toward melodrama, Verdi’s masterworks dominate the standard repertoire a century and a half after their composition.
Verdi's predecessors who influenced his music were Rossini, Bellini, Giacomo Meyerbeer and, most notably, Gaetano Donizetti and Saverio Mercadante. With the exception of Otello and Aida, he was free of Wagner's influence. Although respectful of Gounod, Verdi was careful not to learn anything from the Frenchman whom many of Verdi's contemporaries regarded as the greatest living composer. Some strains in Aida suggest at least a superficial familiarity with the works of the Russian composer Mikhail Glinka, whom Franz Liszt, after his tour of the Russian Empire as a pianist, popularized in Western Europe.
Throughout his career, Verdi rarely utilised the high C in his tenor arias, citing the fact that the opportunity to sing that particular note in front of an audience distracts the performer before and after the note appears. However, he did provide high Cs to Duprez in Jérusalem and to Tamberlick in the original version of La forza del destino. The high C often heard in the aria Di quella pira does not appear in Verdi's score.
Verdi's predecessors who influenced his music were Rossini, Bellini, Giacomo Meyerbeer and, most notably, Gaetano Donizetti and Saverio Mercadante. With the exception of Otello and Aida, he was free of Wagner's influence. Although respectful of Gounod, Verdi was careful not to learn anything from the Frenchman whom many of Verdi's contemporaries regarded as the greatest living composer. Some strains in Aida suggest at least a superficial familiarity with the works of the Russian composer Mikhail Glinka, whom Franz Liszt, after his tour of the Russian Empire as a pianist, popularized in Western Europe.
Throughout his career, Verdi rarely utilised the high C in his tenor arias, citing the fact that the opportunity to sing that particular note in front of an audience distracts the performer before and after the note appears. However, he did provide high Cs to Duprez in Jérusalem and to Tamberlick in the original version of La forza del destino. The high C often heard in the aria Di quella pira does not appear in Verdi's score.
Danny Elfman

Daniel Robert "Danny" Elfman (born May 29, 1953) is an American musician, best known for composing music for television and movies, and leading the rock band Oingo Boingo as singer/songwriter from 1976 until its breakup in 1995. He is a frequent collaborator with long-time friend Tim Burton, and has scored all but two of his films. He was nominated for four Academy Awards and won a Grammy Award for Tim Burton's Batman and an Emmy Award for his Desperate Housewives theme. Elfman also wrote the theme for the video game Fable. He is also famous for creating The Simpsons main title theme, and his role as Jack Skellington's singing voice in The Nightmare Before Christmas. He is the Uncle in-law to actress Jenna Elfman.
Florence and The Machine

Florence and the Machine (stylised as Florence + the Machine) are an English indie rock band, consisting of lead singer Florence Welch, Isabella "Machine" Summers, and a collaboration of other artists who provide backing music. The band's music received praise across the music media, especially from the BBC, before they gained mainstream success. Specifically, the BBC played a large part in their rise to prominence by promoting Florence and the Machine as part of BBC Introducing.
The band's debut album, Lungs, was released on 6 July 2009, and held the number-two position for its first five weeks on the UK Albums Chart. On 17 January 2010, the album reached the top position, after being on the chart for twenty-eight consecutive weeks. As of October 2010, the album had been in the top forty in the United Kingdom for sixty-five consecutive weeks, making it one of the best-selling albums of 2009 and 2010. The group's second studio album, Ceremonials, released in October 2011, debuted at number one in the UK and number six in the US.
Florence and the Machine's sound has been described as a combination of various genres, including rock and soul. Lungs won the MasterCard British Album award at the 2010 BRIT Awards. At the 53rd Grammy Awards, Florence and the Machine were nominated for Best New Artist. Additionally, the band performed at the 2010 MTV Video Music Awards, and the 2010 Nobel Peace Prize Concert.
The band's debut album, Lungs, was released on 6 July 2009, and held the number-two position for its first five weeks on the UK Albums Chart. On 17 January 2010, the album reached the top position, after being on the chart for twenty-eight consecutive weeks. As of October 2010, the album had been in the top forty in the United Kingdom for sixty-five consecutive weeks, making it one of the best-selling albums of 2009 and 2010. The group's second studio album, Ceremonials, released in October 2011, debuted at number one in the UK and number six in the US.
Florence and the Machine's sound has been described as a combination of various genres, including rock and soul. Lungs won the MasterCard British Album award at the 2010 BRIT Awards. At the 53rd Grammy Awards, Florence and the Machine were nominated for Best New Artist. Additionally, the band performed at the 2010 MTV Video Music Awards, and the 2010 Nobel Peace Prize Concert.
Ben Folds

Benjamin Scott Folds (born September 12, 1966 in Winston-Salem, North Carolina) is an American singer and pianist. He originally gained fame as a member of the rock band, Ben Folds Five. Ben has released three solo albums: Fear of Pop: Volume 1, Rockin' the Suburbs, and Ben Folds Live. Fear of Pop was released while Ben Folds Five were still together; Suburbs and Live were released afterwards. Since Fear of Pop is highly experimental and Live is a collection of live solo recordings of mostly songs originally recorded with Ben Folds Five, Rockin' the Suburbs is Ben's first proper solo release. In late 2003 two solo EPs: Speed Graphic and Sunny 16 were released, with a third entitled Super D released in mid-2004. He currently resides in Adelaide, Australia with his wife, Frally Hynes, and two children, Louis and Grace. He tours Japan and the United States, as well as other parts of the world periodically.
Folds also produced and arranged the most recent William Shatner album, Has Been (2004); he previously worked with Shatner on the songs 'In Love' and 'Still in Love' for Fear of Pop.
Folds described his former band, Ben Folds Five, as 'punk rock for sissies,' and his oddball lyrics often contain nuances of depression, melancholy and self-conflict. While he was with the band Ben Folds Five and since his departure, Folds also provided a number of songs for films soundtrack. Some of these include 'Lonely Christmas Eve' for the film How the Grinch Stole Christmas! (2000) and a rendition of the Beatles' 'Golden Slumbers' for the film I Am Sam (2001).
On a planned tour of Australia, Folds teamed up with fellow namesakes Ben Kweller and Ben Lee to travel the country together as The Bens, at the suggestion of a fan on Ben Kweller's official website. The trio also went on to record an four-track EP together, entitled The Bens.
In summer of 2004, Folds co-headlined an American tour with fellow rockers Rufus Wainwright and Guster. His fourth solo album entitled 'Songs for Silverman' is slated for release on April 26, 2005.
Folds also produced and arranged the most recent William Shatner album, Has Been (2004); he previously worked with Shatner on the songs 'In Love' and 'Still in Love' for Fear of Pop.
Folds described his former band, Ben Folds Five, as 'punk rock for sissies,' and his oddball lyrics often contain nuances of depression, melancholy and self-conflict. While he was with the band Ben Folds Five and since his departure, Folds also provided a number of songs for films soundtrack. Some of these include 'Lonely Christmas Eve' for the film How the Grinch Stole Christmas! (2000) and a rendition of the Beatles' 'Golden Slumbers' for the film I Am Sam (2001).
On a planned tour of Australia, Folds teamed up with fellow namesakes Ben Kweller and Ben Lee to travel the country together as The Bens, at the suggestion of a fan on Ben Kweller's official website. The trio also went on to record an four-track EP together, entitled The Bens.
In summer of 2004, Folds co-headlined an American tour with fellow rockers Rufus Wainwright and Guster. His fourth solo album entitled 'Songs for Silverman' is slated for release on April 26, 2005.
George Frideric Handel

George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (/ˈhændəl/; born Georg Friederich Händel (About this soundlisten); 23 February 1685 (O.S.) – 14 April 1759) was a German, later British, Baroque composer who spent the bulk of his career in London, becoming well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, and organ concertos. Handel received important training in Halle and worked as a composer in Hamburg and Italy before settling in London in 1712; he became a naturalised British subject in 1727. He was strongly influenced both by the great composers of the Italian Baroque and by the middle-German polyphonic choral tradition.
Pamela Wedgwood

Born in 1947, Pam’s musical career began with the recorder and piano, and Tenor Horn and Euphonium through the brass band tradition at her school. She then took up the Cello and French Horn, entering Trinity College of Music in London to study Piano, Horn, Cello and composition at the age of sixteen.
Moritz Moszkowski

Moritz (Maurice) Moszkowski (23 August 1854 – 4 March 1925) was a German composer, pianist, and teacher of Polish descent. Ignacy Paderewski said, "After Chopin, Moszkowski best understands how to write for the piano". Although little known today, Moszkowski was well-respected and popular during the late nineteenth century.
His music is brilliant, but has also been described as "devoid of the masculine and the feminine". He wrote over two hundred small-scale piano pieces, which brought him much popularity – notably his set of Spanish Dances, Op. 12, for piano duet (later arranged for solo piano, and for orchestra ). His early Serenade, Op. 15, was world-famous and appeared in many guises, including the song Liebe, kleine Nachtigall. Today he is probably best known for his fifteen Études de Virtuosité, Op. 72, which have been performed by virtuoso pianists such as Vladimir Horowitz and Marc-André Hamelin. Surprisingly, their first complete recording was not until 1970 (by Ilana Vered). Many of his small but brilliant piano pieces, such as Étincelles (Sparks), are used as encore performances at the end of classical concerts.
He also wrote larger scale works including the Piano Concerto in E major, Op. 59 (1898), the Violin Concerto in C major, Op. 30, three orchestral suites (Opp. 39, 47, 79), and a symphonic poem Jeanne d'Arc, Op. 19.
He wrote the opera Boabdil der letzte Maurenkönig, Op. 49, on the historical theme of the capture of Granada. It was premiered at the Berlin Court Opera on 21 April 1892, and appeared in Prague and New York the following year. It did not stay in the repertoire, but its ballet music was very popular for a number of years. He wrote a three-act ballet Laurin in 1896.
His music is brilliant, but has also been described as "devoid of the masculine and the feminine". He wrote over two hundred small-scale piano pieces, which brought him much popularity – notably his set of Spanish Dances, Op. 12, for piano duet (later arranged for solo piano, and for orchestra ). His early Serenade, Op. 15, was world-famous and appeared in many guises, including the song Liebe, kleine Nachtigall. Today he is probably best known for his fifteen Études de Virtuosité, Op. 72, which have been performed by virtuoso pianists such as Vladimir Horowitz and Marc-André Hamelin. Surprisingly, their first complete recording was not until 1970 (by Ilana Vered). Many of his small but brilliant piano pieces, such as Étincelles (Sparks), are used as encore performances at the end of classical concerts.
He also wrote larger scale works including the Piano Concerto in E major, Op. 59 (1898), the Violin Concerto in C major, Op. 30, three orchestral suites (Opp. 39, 47, 79), and a symphonic poem Jeanne d'Arc, Op. 19.
He wrote the opera Boabdil der letzte Maurenkönig, Op. 49, on the historical theme of the capture of Granada. It was premiered at the Berlin Court Opera on 21 April 1892, and appeared in Prague and New York the following year. It did not stay in the repertoire, but its ballet music was very popular for a number of years. He wrote a three-act ballet Laurin in 1896.
Justin Timberlake

Justin Randall Timberlake (born January 31, 1981) is an American pop singer-songwriter, record producer, dancer and actor. He has won six Grammy Awards as well as an Emmy Award.
Justin Timberlake came to fame as one of the lead singers of pop "boy band" (or "vocal harmony group") 'N Sync, whose launch was financed by Lou Pearlman. In 2002, he released his debut solo album, Justified, which sold more than 7 million copies worldwide. Timberlake's second solo release, FutureSex/LoveSounds, was released in 2006 with the U.S. number-one hit singles "SexyBack", "My Love", and "What Goes Around.../...Comes Around". The album also spawned three additional U.S. top twenty hits ("Summer Love", "LoveStoned", and "Until the End of Time"). As of January 2008, FutureSex/LoveSounds has sold more than 8.6 million copies. With his first two albums, Timberlake has sold more than 18 million records worldwide alone, as well as more than 50 million copies as one of the two lead singers in 'N Sync. His other ventures include record label Tennman Records, fashion label William Rast, and the restaurants Destino and Southern Hospitality.
Justin Timberlake came to fame as one of the lead singers of pop "boy band" (or "vocal harmony group") 'N Sync, whose launch was financed by Lou Pearlman. In 2002, he released his debut solo album, Justified, which sold more than 7 million copies worldwide. Timberlake's second solo release, FutureSex/LoveSounds, was released in 2006 with the U.S. number-one hit singles "SexyBack", "My Love", and "What Goes Around.../...Comes Around". The album also spawned three additional U.S. top twenty hits ("Summer Love", "LoveStoned", and "Until the End of Time"). As of January 2008, FutureSex/LoveSounds has sold more than 8.6 million copies. With his first two albums, Timberlake has sold more than 18 million records worldwide alone, as well as more than 50 million copies as one of the two lead singers in 'N Sync. His other ventures include record label Tennman Records, fashion label William Rast, and the restaurants Destino and Southern Hospitality.
Tori Amos

Tori Amos (born Myra Ellen Amos on August 22, 1963) is a pianist and singer-songwriter of dual British and American citizenship. She is married to English sound engineer Mark Hawley, with whom she has one child, Natashya "Tash" Lórien Hawley, born on September 5, 2000.
Amos was at the forefront of a number of female singer-songwriters in the early 1990s and was noteworthy early in her career as one of the few alternative rock performers to use a piano as her primary instrument. She is known for emotionally intense songs that cover a wide range of subjects including sexuality, religion and personal tragedy. Some of her charting singles include "Crucify", "Silent All These Years", "Cornflake Girl", "Caught a Lite Sneeze", "Professional Widow", "Spark", and "A Sorta Fairytale".
Amos had sold 12 million records worldwide as of 2005 and has also enjoyed a large cult following. Having a history of making eccentric and at times ribald comments during concerts and interviews, she has earned a reputation for being highly idiosyncratic. As a social commentator and sometimes activist, some of the topics she has been most vocal about include feminism, religion, and sexuality.
Amos was at the forefront of a number of female singer-songwriters in the early 1990s and was noteworthy early in her career as one of the few alternative rock performers to use a piano as her primary instrument. She is known for emotionally intense songs that cover a wide range of subjects including sexuality, religion and personal tragedy. Some of her charting singles include "Crucify", "Silent All These Years", "Cornflake Girl", "Caught a Lite Sneeze", "Professional Widow", "Spark", and "A Sorta Fairytale".
Amos had sold 12 million records worldwide as of 2005 and has also enjoyed a large cult following. Having a history of making eccentric and at times ribald comments during concerts and interviews, she has earned a reputation for being highly idiosyncratic. As a social commentator and sometimes activist, some of the topics she has been most vocal about include feminism, religion, and sexuality.
Jim Steinman

James Richard Steinman is an American composer, lyricist, record producer, and playwright. He has also worked as an arranger, pianist and singer. His work has included songs in the adult contemporary, rock and roll, dance, pop, musical theater and film score genres
Hiromi Uehara

Hiromi Uehara (上原ひろみ, born 26 March 1979), known as Hiromi, is a jazz composer and pianist born in Hamamatsu, Japan. She is known for her virtuosic technique, energetic live performances and blend of musical genres such as post-bop, progressive rock, classical and fusion in her compositions.
Elton John

Sir Elton Hercules John CBE (born Reginald Kenneth Dwight on 25 March 1947) is an English pop/rock singer, composer and pianist.
In his four-decade career, John has been one of the dominant forces in rock and popular music, especially during the 1970s. He has sold over 200 million records, making him one of the most successful artists of all time. He has more than 50 Top 40 hits including seven consecutive No. 1 U.S. albums, 59 Top 40 singles, 16 Top 10, four No. 2 hits, and nine No. 1 hits. He has won five Grammy awards and one Academy Award. His success has had a profound impact on popular music and has contributed to the continued popularity of the piano in rock and roll. In 2004, Rolling Stone ranked him #49 on their list of the 100 greatest artists of all time.
Some of the characteristics of John's musical talent include an ability to quickly craft melodies for the lyrics of songwriting partner Bernie Taupin, his former rich tenor (now baritone) voice, his classical and gospel-influenced piano, the aggressive orchestral arrangements of Paul Buckmaster among others and the flamboyant fashions, outlandishly excessive eyeglasses, and on-stage showmanship, especially evident during the 1970s.
John was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1994. He has been heavily involved in the fight against AIDS since the late 1980s, and was knighted in 1998. He entered into a civil partnership with David Furnish on 21 December 2005 and continues to be a champion for LGBT social movements. On April 9, 2008, John held a benefit concert for Hillary Clinton's presidential campaign, raising $2.5 million.
In his four-decade career, John has been one of the dominant forces in rock and popular music, especially during the 1970s. He has sold over 200 million records, making him one of the most successful artists of all time. He has more than 50 Top 40 hits including seven consecutive No. 1 U.S. albums, 59 Top 40 singles, 16 Top 10, four No. 2 hits, and nine No. 1 hits. He has won five Grammy awards and one Academy Award. His success has had a profound impact on popular music and has contributed to the continued popularity of the piano in rock and roll. In 2004, Rolling Stone ranked him #49 on their list of the 100 greatest artists of all time.
Some of the characteristics of John's musical talent include an ability to quickly craft melodies for the lyrics of songwriting partner Bernie Taupin, his former rich tenor (now baritone) voice, his classical and gospel-influenced piano, the aggressive orchestral arrangements of Paul Buckmaster among others and the flamboyant fashions, outlandishly excessive eyeglasses, and on-stage showmanship, especially evident during the 1970s.
John was inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame in 1994. He has been heavily involved in the fight against AIDS since the late 1980s, and was knighted in 1998. He entered into a civil partnership with David Furnish on 21 December 2005 and continues to be a champion for LGBT social movements. On April 9, 2008, John held a benefit concert for Hillary Clinton's presidential campaign, raising $2.5 million.
No Doubt

No Doubt is a rock band from Anaheim, California, United States, founded in 1986. The ska-rock sound of its first album failed to make waves due to the popularity of the grunge movement at the time. The band's diamond-certified album Tragic Kingdom helped to launch the ska revival of the 1990s, and "Don't Speak", the third single from the album, set a record when it spent sixteen weeks at the number one spot on the Billboard Hot 100 Airplay chart, later broken by the Goo Goo Dolls' "Iris".
The group released its next album, Return of Saturn, four years later, but despite positive reviews, the album was considered a commercial failure. Fifteen months later, the band reappeared with Rock Steady, which incorporated reggae and dancehall music into their work. The album was primarily recorded in Jamaica and featured collaborations with Jamaican artists Bounty Killer, Sly and Robbie, and Lady Saw. The album produced two Grammy-winning singles, "Hey Baby" and "Underneath It All".
No Doubt released the compilation The Singles 1992-2003 and box set Boom Box in 2003, both of which contained a cover version of the Talk Talk synthpop song "It's My Life". Frontwoman Gwen Stefani launched her solo career the next year with several collaborations, including bandmate Tony Kanal and Neptune Pharrell, while guitarist Tom Dumont began his side project, Invincible Overlord. During its career, the band has won two Grammy Awards and sold 27 million records worldwide to date.
The group released its next album, Return of Saturn, four years later, but despite positive reviews, the album was considered a commercial failure. Fifteen months later, the band reappeared with Rock Steady, which incorporated reggae and dancehall music into their work. The album was primarily recorded in Jamaica and featured collaborations with Jamaican artists Bounty Killer, Sly and Robbie, and Lady Saw. The album produced two Grammy-winning singles, "Hey Baby" and "Underneath It All".
No Doubt released the compilation The Singles 1992-2003 and box set Boom Box in 2003, both of which contained a cover version of the Talk Talk synthpop song "It's My Life". Frontwoman Gwen Stefani launched her solo career the next year with several collaborations, including bandmate Tony Kanal and Neptune Pharrell, while guitarist Tom Dumont began his side project, Invincible Overlord. During its career, the band has won two Grammy Awards and sold 27 million records worldwide to date.
Elgar

Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, OM, GCVO (2 June 1857 – 23 February 1934) was an English composer. He is known for such works as the Enigma Variations, the Pomp and Circumstance Marches, The Dream of Gerontius, concertos for violin and cello, and two symphonies. He also composed oratorios, chamber music and songs. He was appointed Master of the King's Musick in 1924.
Richard Strauss

Richard Georg Strauss (German pronunciation: ; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wagner and Franz Liszt. Along with Gustav Mahler, he represents the late flowering of German Romanticism after Wagner, in which pioneering subtleties of orchestration are combined with an advanced harmonic style.
Francesco Manfredini
Francesco Onofrio Manfredini (22 June 1684 – 6 October 1762) was an Italian Baroque composer, violinist, and church musician.
He was born at Pistoia to a trombonist. He studied violin with Giuseppe Torelli in Bologna, then a part of the Papal States, a leading figure in the development of the concerto grosso. He also took instruction in composition from Giacomo Antonio Perti, maestro di cappella of the Basilica of San Petronio from 1696 when the orchestra was temporarily disbanded.
Although he composed oratorios, only his secular works remain in the repertoire. A contemporary of Johann Sebastian Bach and Antonio Vivaldi, his extant work shows the influence of the latter.
He was born at Pistoia to a trombonist. He studied violin with Giuseppe Torelli in Bologna, then a part of the Papal States, a leading figure in the development of the concerto grosso. He also took instruction in composition from Giacomo Antonio Perti, maestro di cappella of the Basilica of San Petronio from 1696 when the orchestra was temporarily disbanded.
Although he composed oratorios, only his secular works remain in the repertoire. A contemporary of Johann Sebastian Bach and Antonio Vivaldi, his extant work shows the influence of the latter.
Antonio Lauro

Antonio Lauro was a Venezuelan musician, considered to be one of the foremost South American composers for the guitar in the 20th century.
Andrew Lloyd Webber

Andrew Lloyd Webber, Baron Lloyd-Webber (born 22 March 1948) is an English composer of musical theatre, the elder son of organist William Lloyd Webber and brother of the cellist Julian Lloyd Webber. Lloyd Webber started composing at the age of six, and published his first piece at the age of nine.
Lloyd Webber has achieved great popular success, with several musicals that have run for more than a decade both in the West End and on Broadway. He has composed 13 musicals, a song cycle, a set of variations, two film scores, and a Latin Requiem Mass. He has also gained a number of honours, including a knighthood in 1992, followed by a peerage from the British Government for services to Music, seven Tony Awards (and 40 nominations), three Grammy Awards (with an additional 60 nominations), an Academy Award (two other nominations), seven Olivier Awards (with 100 nominations), a Golden Globe, and the Kennedy Center Honors in 2006. Several of his songs, notably "The Music of the Night" from The Phantom of the Opera, "I Don't Know How to Love Him" from Jesus Christ Superstar, "Don't Cry for Me, Argentina" from Evita, "Any Dream Will Do" from Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat and "Memory" from Cats have been widely recorded and were hits outside of their parent musicals. His company, the Really Useful Group, is one of the largest theatre operators in London.
Producers in several parts of the UK have staged productions, including national tours, of Lloyd Webber's musicals under licence from the Really Useful Group. According to britishhitsongwriters.com, he is the one hundredth most successful songwriter in U.K. singles chart history, based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
Lloyd Webber has achieved great popular success, with several musicals that have run for more than a decade both in the West End and on Broadway. He has composed 13 musicals, a song cycle, a set of variations, two film scores, and a Latin Requiem Mass. He has also gained a number of honours, including a knighthood in 1992, followed by a peerage from the British Government for services to Music, seven Tony Awards (and 40 nominations), three Grammy Awards (with an additional 60 nominations), an Academy Award (two other nominations), seven Olivier Awards (with 100 nominations), a Golden Globe, and the Kennedy Center Honors in 2006. Several of his songs, notably "The Music of the Night" from The Phantom of the Opera, "I Don't Know How to Love Him" from Jesus Christ Superstar, "Don't Cry for Me, Argentina" from Evita, "Any Dream Will Do" from Joseph and the Amazing Technicolor Dreamcoat and "Memory" from Cats have been widely recorded and were hits outside of their parent musicals. His company, the Really Useful Group, is one of the largest theatre operators in London.
Producers in several parts of the UK have staged productions, including national tours, of Lloyd Webber's musicals under licence from the Really Useful Group. According to britishhitsongwriters.com, he is the one hundredth most successful songwriter in U.K. singles chart history, based on weeks that his compositions have spent on the chart.
ZUN

ZUN" and is the main programmer, scriptwriter, graphic artist, and music composer. His real name is Jun'ya Ōta
Saint Saens
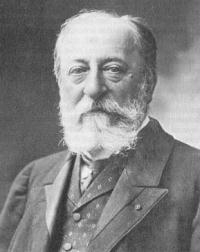
Charles-Camille Saint-Saëns (9 October 1835 – 16 December 1921) was a French composer, organist, conductor, and pianist, known especially for The Carnival of the Animals, Danse Macabre, Samson and Delilah, Havanaise, Introduction and Rondo capriccioso, and his Symphony No. 3 (Organ Symphony).
Raimonds Pauls

Ojārs Raimonds Pauls is a Latvian composer and piano player who is well known in Latvia, Russia, post-Soviet countries and world-wide.
Yiruma

Yiruma (born February 15 1978, Seoul, Korea) is a South Korean piano music composer. He is married to Son Hye-im.
Yiruma is well-known throughout the world, and his albums are sold all over Asia, as well as the United States and Europe. His most famous pieces are "Kiss the Rain", and also "River Flows in You". These pieces are widely mistaken for being associated with the movie Twilight. Although he formerly held dual citizenship as a citizen of the United Kingdom and South Korea, in July 2006 he gave up his British citizenship and entered the Republic of Korea Navy to begin his military service, which is compulsory for all male South Koreans. He has lived in Osaka, Japan for 5 years to promote album sales before giving up his dual citizenship.
Yiruma is well-known throughout the world, and his albums are sold all over Asia, as well as the United States and Europe. His most famous pieces are "Kiss the Rain", and also "River Flows in You". These pieces are widely mistaken for being associated with the movie Twilight. Although he formerly held dual citizenship as a citizen of the United Kingdom and South Korea, in July 2006 he gave up his British citizenship and entered the Republic of Korea Navy to begin his military service, which is compulsory for all male South Koreans. He has lived in Osaka, Japan for 5 years to promote album sales before giving up his dual citizenship.
ABBA

ABBA was a Swedish Eurovision Song Contest-winning pop music group active between 1972 and 1982. Benny Andersson, Björn Ulvaeus, Anni-Frid Lyngstad (Frida), Agnetha Fältskog are in ABBA. They topped the charts worldwide from the mid-1970s to the early 1980s. The name "ABBA" is an acronym formed from the first letters of each of the group member's given name (Agnetha, Björn, Benny, Anni-Frid).
ABBA gained immense international popularity employing catchy song hooks, simple lyrics, and a Wall of Sound achieved by overdubbing the female singers' voices in multiple harmonies. As their popularity grew, they were sought-after to tour Europe, Australia, and North America, drawing crowds of near-hysterical fans ("ABBAholics"), notably in Australia. Touring became a contentious issue, being particularly unpopular with Agnetha, but they continued to release studio albums to great commercial success. At the height of their popularity, however, both marriages of the band members (Benny with Frida, and Björn with Agnetha) failed, and the relationship changes were reflected in their music, as they produced more thoughtful lyrics with different compositions.
They remain a fixture of radio playlists and are one of the world's best selling bands, having sold around 400 million records world wide; The music of ABBA has been re-arranged into the successful musical Mamma Mia! that has toured worldwide and a movie version was released in July 2008. All four of the former members of ABBA were present at the Stockholm premieres of both the musical (2005) and the film (2008). The film première took place at the Benny Andersson-owned Rival theatre at Mariatorget, Stockholm on 4 July 2008.
ABBA gained immense international popularity employing catchy song hooks, simple lyrics, and a Wall of Sound achieved by overdubbing the female singers' voices in multiple harmonies. As their popularity grew, they were sought-after to tour Europe, Australia, and North America, drawing crowds of near-hysterical fans ("ABBAholics"), notably in Australia. Touring became a contentious issue, being particularly unpopular with Agnetha, but they continued to release studio albums to great commercial success. At the height of their popularity, however, both marriages of the band members (Benny with Frida, and Björn with Agnetha) failed, and the relationship changes were reflected in their music, as they produced more thoughtful lyrics with different compositions.
They remain a fixture of radio playlists and are one of the world's best selling bands, having sold around 400 million records world wide; The music of ABBA has been re-arranged into the successful musical Mamma Mia! that has toured worldwide and a movie version was released in July 2008. All four of the former members of ABBA were present at the Stockholm premieres of both the musical (2005) and the film (2008). The film première took place at the Benny Andersson-owned Rival theatre at Mariatorget, Stockholm on 4 July 2008.
George Gershwin

George Gershwin (September 26, 1898 – July 11, 1937) was an American composer. He wrote most of his vocal and theatrical works in collaboration with his elder brother, lyricist Ira Gershwin. George Gershwin composed songs both for Broadway and for the classical concert hall. He also wrote popular songs with success.
Many of his compositions have been used on television and in numerous films, and many became jazz standards. The jazz singer Ella Fitzgerald recorded many of the Gershwins' songs on her 1959 Gershwin Songbook (arranged by Nelson Riddle). Countless singers and musicians have recorded Gershwin songs, including Fred Astaire, Louis Armstrong, Al Jolson, Bobby Darin, Art Tatum, Bing Crosby, Janis Joplin, John Coltrane, Frank Sinatra, Billie Holiday, Sam Cooke, Miles Davis, Herbie Hancock, Madonna, Judy Garland, Julie Andrews, Barbra Streisand, Marni Nixon, Natalie Cole, Patti Austin, Nina Simone, Maureen McGovern, John Fahey, The Residents, Than & Sam, Sublime, and Sting. A residential building is named after him on the Stony Brook University campus.
Many of his compositions have been used on television and in numerous films, and many became jazz standards. The jazz singer Ella Fitzgerald recorded many of the Gershwins' songs on her 1959 Gershwin Songbook (arranged by Nelson Riddle). Countless singers and musicians have recorded Gershwin songs, including Fred Astaire, Louis Armstrong, Al Jolson, Bobby Darin, Art Tatum, Bing Crosby, Janis Joplin, John Coltrane, Frank Sinatra, Billie Holiday, Sam Cooke, Miles Davis, Herbie Hancock, Madonna, Judy Garland, Julie Andrews, Barbra Streisand, Marni Nixon, Natalie Cole, Patti Austin, Nina Simone, Maureen McGovern, John Fahey, The Residents, Than & Sam, Sublime, and Sting. A residential building is named after him on the Stony Brook University campus.
Chopin

Frédéric Chopin (1 March 1810 – 17 October 1849) was a Polish composer and virtuoso pianist of the Romantic period. He is widely regarded as the greatest Polish composer, and ranks as one of music's greatest tone poets.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
He was born in the village of Żelazowa Wola, in the Duchy of Warsaw, to a Polish mother and French-expatriate father, and in his early life was regarded as a child-prodigy pianist. In November 1830, at the age of 20, Chopin went abroad; following the suppression of the Polish November Uprising of 1830–31, he became one of many expatriates of the Polish "Great Emigration."
In Paris, he made a comfortable living as a composer and piano teacher, while giving few public performances. A Polish patriot,
Chopin's extant compositions were written primarily for the piano as a solo instrument. Though technically demanding, Chopin's style emphasizes nuance and expressive depth rather than virtuosity. Chopin invented musical forms such as the ballade and was responsible for major innovations in forms such as the piano sonata, waltz, nocturne, étude, impromptu and prelude. His works are mainstays of Romanticism in 19th-century classical music.
 Sheet Music Exchange is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.
Sheet Music Exchange is a web site for those who wants to access popular sheet music easily,
letting them download the sheet music for free for trial purposes.
It's completely free to download and try the listed sheet music, but you have to delete the files after 24 hours of trial period.
Don't forget, if you like the piece of music you have just learned playing,
treat the artist with respect, and go buy the original sheet music.